

Disclosure: This post includes affiliate links; I may receive compensation if you purchase products or services from the different links provided in this article. Hello, Java programmers! Over the past few years, I have been sharing a lot of Java Interview questions, answers, and discussion individually. Many of my readers have requested that I bring them together so that they can have them in the same spot for their interview preparation. This post is the result of that. This article contains more than 50 Java Interview questions and answers covering all important topics like Core Java fundamentals, Java Collection Framework, Java Multithreading and Concurrency, Java IO, JDBC, JVM Internals, Coding Problems, Object-Oriented programming, etc. These questions are picked up from various Java interviews which I have given and few are shared by my friends, readers, and other people from their own experience. They are, by no means, very difficult. You might have seen them already in your phone or face-to-face round of interviews. The questions are also very useful to review important Java topics like core Java concepts, multithreading, lambdas, Streams, and collections. I have also shared some useful resources for further learning and improvement like The Complete Java MasterClass course on Udemy which you can join to brush up and fill gaps in your Java skills. I have also written books on Java Interview preparation like "Grokking the Java Interview", and Grokking the Spring Boot Interviews, where I have shared a lot of questions for Java developers. If you are preparing for Java interviews this year you can also get my Java + Spring Interview + SQL Bundle on Gumroad, use code friends20 to get a 20% discount also So what are we waiting for? Here is the list of some of the most frequently asked Java questions in interviews for both beginner and experienced Java developers.
So, without wasting any more of your time, here is my list of some of the frequently asked Core Java Interview Questions for beginner programmers. This list focuses on beginners and less experienced devs, like someone with 2 to 3 years of experience in Java. 1) How does Java achieve platform independence? (answer)
hint: bytecode and Java Virtual Machine
answer - Java achieves platform independence by producing bytecode and then running on Java virtual Machine which convert these bytecode to planform dependent machine code. Since JVM is different for different platform, I mean for Windows you have separate JRE (Which includes JVM) and for Linux you will have separate JRE. Since Java code are not compiled to native machine code instead they compiled to bytecode which makes them platform independent. 2) What is **ClassLoader** in Java? (answer)
hint: part of JVM that loads bytecodes for classes. You can write your own.
answer: In Java, code is encapsulated inside class because Java is an object oriented programming. Your program is written inside class and in order to execute them JVM loads these classes which contains your code. The JVM component which is responsible for loading classes are called classloaders. They are three main classloaders exists in, the bootstrap classloader, the extension classloader and the application classloader. Here is a nice diagram which shows the function of each of these classloader Java: 
hint: you can use the bitwise operator, like bitwise AND, remember, even the number has zero at the end in binary format and an odd number has 1 in the end. 4) Difference between **ArrayList** and **HashSet** in Java? (answer)
hint: all differences between List and Set are applicable here, e.g. ordering, duplicates, random search, etc. See Java Fundamentals: Collections by Richard Warburton to learn more about ArrayList, HashSet and other important Collections in Java. 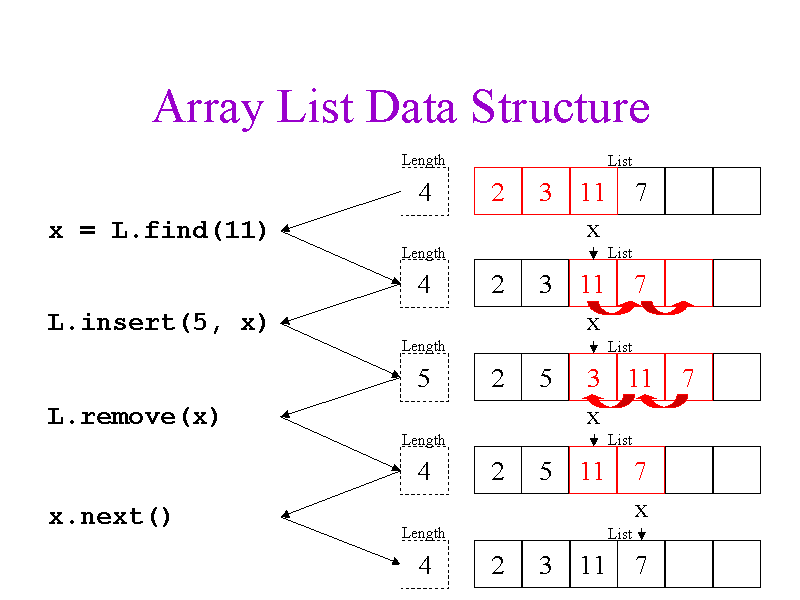 5) What is double checked locking in Singleton? (answer)
5) What is double checked locking in Singleton? (answer)
hint: two-time check whether instances is initialized or not, first without locking and second with locking. 6) How do you create thread-safe Singleton in Java? (answer)
hint: many ways, like using Enum or by using double-checked locking pattern or using a nested static class. 7) Difference between Serializable and Externalizable in Java? (answer)
hint: Externalizable gives you more control over the Serialization process. 8) When to use a transient variable in Java? (answer)
hint: when you want to make a variable non-serializable in a class, which implements the Serializable interface. In other words, you can use it for a variable whose value you don't want to save. See The Complete Java MasterClass to learn about transient variables in Java. 9) Difference between the transient and volatile variable in Java? (answer)
hint: totally different, one used in the context of serialization while the other is used in concurrency. 10) When to use the volatile variable in Java? (answer)
hint: when you need to instruct the JVM that a variable can be modified by multiple threads and give hint to JVM that does not cache its value. 11) Can we override the private method in Java? (answer)
hint: No, because it's not visible in the subclass, a primary requirement for overriding a method in Java. 12) Difference between **Hashtable** and **HashMap** in Java? (answer**)
**hint: several but most important is Hashtable , which is synchronized, while HashMap is not. It's also legacy and slow as compared to HashMap . 13) Difference between **List** and **Set** in Java? (answer)
hint: List is ordered and allows duplicate. Set is unordered and doesn't allow duplicate elements. 14) Difference between **ArrayList** and **Vector** in Java (answer)
hint: Many, but most important is that ArrayList is non-synchronized and fast while Vector is synchronized and slow. It's also legacy class like Hashtable . 15) Difference between **Hashtable** and **ConcurrentHashMap** in Java? (answer)
hint: more scalable. See Java Fundamentals: Collections by Richard Warburton to learn more. 16) How does **ConcurrentHashMap** achieve scalability? (answer)
hint: by dividing the map into segments and only locking during the write operation. 17) Which two methods you will override for an **Object** to be used as **Key** in **HashMap** ? (answer)
hint: equals and hashcode 18) Difference between wait and sleep in Java? (answer)\
hint: The wait() method releases the lock or monitor, while sleep doesn't. 19) Difference between **notify** and **notifyAll** in Java? (answer)
hint: notify notifies one random thread is waiting for that lock while notifyAll inform to all threads waiting for a monitor. If you are certain that only one thread is waiting then use notify , or else notifyAll is better. See Threading Essentials Mini-Courseby Java Champion Heinz Kabutz to learn more about threading basics. 20) Why you override hashcode, along with **equals()** in Java? (answer)
hint: to be compliant with equals and hashcode contract, which is required if you are planning to store your object into collection classes, e.g. HashMap or ArrayList . 21) What is the load factor of **HashMap** means? (answer)
hint: The threshold that triggers the re-sizing of HashMap is generally 0.75, which means HashMap resize itself if it's 75 percent full. 22) Difference between **ArrayList** and **LinkedList** in Java? (answer)
hint: same as an array and linked list, one allows random search while other doesn't. Insertion and deletion easy on the linked list but a search is easy on an array. See Java Fundamentals: Collections, Richard Warburton's course on Pluralsight, to learn more about essential Collection data structure in Java. 23) Difference between **CountDownLatch** and **CyclicBarrier** in Java? (answer)
hint: You can reuse CyclicBarrier after the barrier is broken but you cannot reuse CountDownLatch after the count reaches to zero. 24) When do you use **Runnable** vs **Thread** in Java? (answer)
hint: always 25) What is the meaning of Enum being type-safe in Java? (answer)
hint: It means you cannot assign an instance of different Enum type to an Enum variable. e.g. if you have a variable like DayOfWeek day then you cannot assign it value from DayOfMonth enum. 26) How does Autoboxing of Integer work in Java? (answer)
hint: By using the valueOf() method in Java. 27) Difference between **PATH** and **Classpath** in Java? (answer)
hint: PATH is used by the operating system while Classpath is used by JVM to locate Java binary, e.g. JAR files or Class files. SeeJava Fundamentals: The Core Platform to learn more about PATH , Classpath , and other Java environment variable. 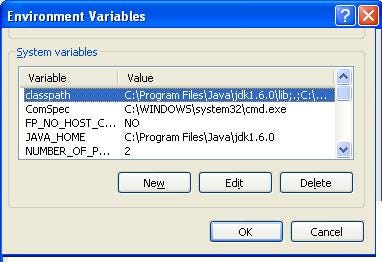 28) Difference between method overloading and overriding in Java? (answer)
28) Difference between method overloading and overriding in Java? (answer)
hint: Overriding happens at subclass while overloading happens in the same class. Also, overriding is a runtime activity while overloading is resolved at compile time. 29) How do you prevent a class from being sub-classed in Java? (answer)\
hint: just make its constructor private 30) How do you restrict your class from being used by your client? (answer)\
hint: make the constructor private or throw an exception from the constructor 31) Difference between **StringBuilder** and **StringBuffer** in Java? (answer)
hint: StringBuilder is not synchronized while StringBuffer is synchronized. 32) Difference between Polymorphism and Inheritance in Java? (answer)
hint: Inheritance allows code reuse and builds the relationship between class, which is required by Polymorphism, which provides dynamic behavior. See Object Oriented Java Programming: Data Structures and Beyond Specialization on Coursera, to learn more about OOP features. One of the most in-depth course for beginners.  By the way, if you find Coursera courses useful, which they are because they are created by reputed companies and universities around the world, I suggest you join the Coursera Plus, a subscription plan from Coursera which gives you unlimited access to their most popular courses, specialization, professional certificate, and guided projects. It cost around $399/year but its complete worth of your money as you get unlimited certificates. 33) Can we override static method in Java? (answer)\
By the way, if you find Coursera courses useful, which they are because they are created by reputed companies and universities around the world, I suggest you join the Coursera Plus, a subscription plan from Coursera which gives you unlimited access to their most popular courses, specialization, professional certificate, and guided projects. It cost around $399/year but its complete worth of your money as you get unlimited certificates. 33) Can we override static method in Java? (answer)\
hint: No, because overriding resolves at runtime while static method call is resolved at compile time. 34) Can we access the private method in Java? (answer)\
hint: yes, in the same class but not outside the class 35) Difference between interface and abstract class in Java? (answer)
hint: from Java 8, the difference is blurred. However, a Java class can still implement multiple interfaces but can only extend one class. 36) Difference between DOM and SAX parser in Java? (answer)\
hint: DOM loads whole XML File in memory while SAX doesn't. It is an event-based parser and can be used to parse a large file, but DOM is fast and should be preferred for small files. 37) Difference between throw and throws keyword in Java? (answer)\
hint: throws declare what exception a method can throw in case of error but throw keyword actually throws an exception. See Java Fundamentals: Exception Handling to learn more about Exception handling in Java. 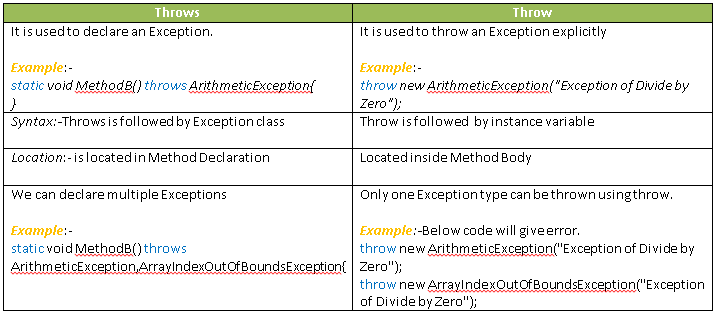 38) Difference between fail-safe and fail-fast iterators in Java? (answer)
38) Difference between fail-safe and fail-fast iterators in Java? (answer)
hint: fail-safe doesn't throw ConcurrentModificationException while fail-fast does whenever they detect an outside change on the underlying collection while iterating over it. 39) Difference between Iterator and Enumeration in Java? (answer)
hint: Iterator also gives you the ability to remove an element while iterating while Enumeration doesn't allow that. 40) What is **IdentityHashMap** in Java? (answer)
hint: A Map , which uses the == equality operator to check equality instead of the equals() method. 41) What is the **String** pool in Java? (answer)
hint: A pool of String literals. Remember it's moved to heap from perm gen space in JDK 7. 42) Can a **Serializable** class contains a non-serializable field in Java? (answer**)
**hint: Yes, but you need to make it either static or transient. 43) Difference between this and super in Java? (answer)
hint: this refers to the current instance while super refers to an instance of the superclass. 44) Difference between **Comparator** and **Comparable** in Java? (answer)\
hint: Comparator defines custom ordering while Comparable defines the natural order of objects, e.g. the alphabetic order for String . SeeThe Complete Java MasterClass to learn more about sorting in Java. 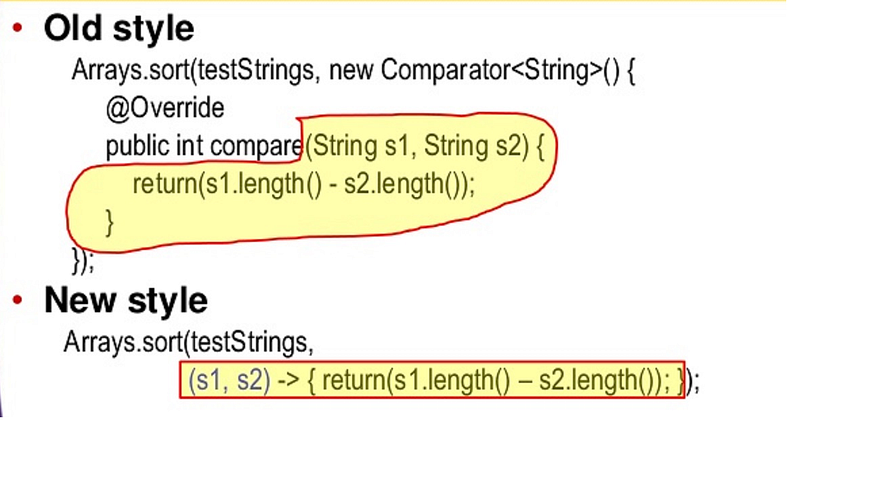 45) Difference between **java.util.Date** and **java.sql.Date** in Java? (answer)
45) Difference between **java.util.Date** and **java.sql.Date** in Java? (answer)
hint: former contains both date and time while later contains only date part. 46) Why wait and notify method are declared in **Object** class in Java? (answer)
hint: because they require lock which is only available to an object. 47) Why Java doesn't support multiple inheritances? (answer)
hint: It doesn't support because of a bad experience with C++, but with Java 8, it does in some sense --- only multiple inheritances of Type are not supported in Java now. 48) Difference between checked and unchecked Exception in Java? (answer)
hint: In case of checked, you must handle exception using catch block, while in case of unchecked, it's up to you; compile will not bother you. 49) Difference between Error and Exception in Java? (answer)
hint: I am tired of typing please check the answer 50) Difference between Race condition and Deadlock in Java? (answer)
hint: both are errors that occur in a concurrent application, one occurs because of thread scheduling while others occur because of poor coding. See Multithreading and Parallel Computing in Java to learn more about deadlock, Race Conditions, and other multithreading issues.
Thanks, You made it to the end of the article . Good luck with your programming interview! It's certainly not going to be easy, but these questions will certainly help you. It will also encourage you to learn more.
If you like this article, then please share with your friends and colleagues, and don't forget to follow javinpaul on Twitter!
P.S. --- If you need some FREE resources to learn Java, you can check out this list of my favorite free Java courses to start your preparation.
P. S. S. --- I have not provided the answer to the interview questions shared in the image " How many String objects are created in the code?" can you guess and explain?
And, If you are preparing for Java interviews this year you can also get my Java + Spring Interview + SQL Bundle on Gumroad, use code friends20 to get a 20% discount also